
(text and background only visible when logged in)
Using an approach unlike any other in higher education, Georgia Tech’s College of Engineering has created a digital sandbox for students to understand and use artificial intelligence in the classroom.
The AI Makerspace is a supercomputer hub that gives students access to computing resources typically available only to researchers or tech companies. It means hands-on experience for our students, deepening their skills and preparing them to be the new generation of AI professionals.
With the resources in the AI Makerspace, the College can redesign courses to incorporate practical AI tools and develop new ones that impart the essential principles of AI to all students.
The initiative is in collaboration with NVIDIA, one of the country’s largest suppliers of AI hardware and software — and a substantial investment. Students and faculty receive support through NVIDIA Deep Learning Institute resources, including faculty-run NVIDIA workshops, certifications, a university ambassador program, curriculum-aided teaching kits, and a developer community network.
The AI Makerspace also enables Georgia Tech to enhance or redesign courses to incorporate practical AI tools, along with develop new courses — both foundational and advanced — that impart the essential principles of AI to all students.
The partnership between Georgia Tech and NVIDIA signifies a substantial investment. The allocated funds will be utilized for technology, including NVIDIA graphics processing units (GPUs), and infrastructure. Students and faculty will receive support through NVIDIA Deep Learning Institute resources, including faculty-run NVIDIA workshops, certifications, a university ambassador program, curriculum-aided teaching kits, and a developer community network.
The collaboration is part of the College’s commitment to nurturing a vibrant AI-powered university that will shape the future generation of AI professionals.
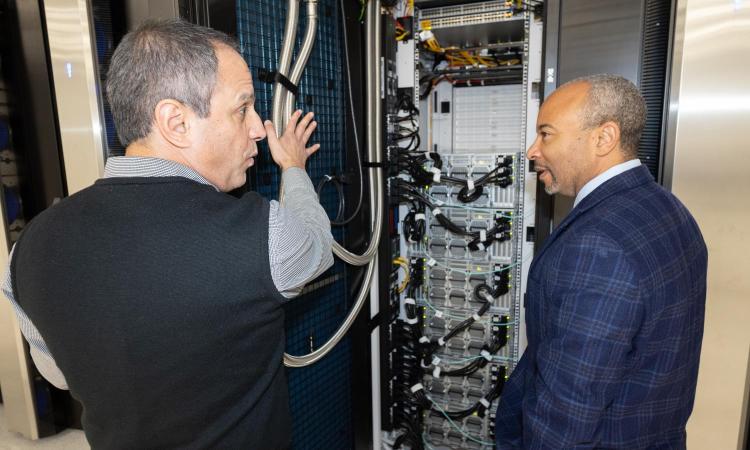

Georgia Tech Unveils New AI Makerspace
By giving students access to powerful supercomputers, Georgia Tech will teach AI to undergraduates in a way unlike any other university in the nation.
(text and background only visible when logged in)
(text and background only visible when logged in)
What Sets the Georgia Tech AI Makerspace Apart?

Educational Empowerment
In an era where AI is increasingly ingrained in our daily lives, the AI Makerspace democratizes access to heavyweight computing resources.
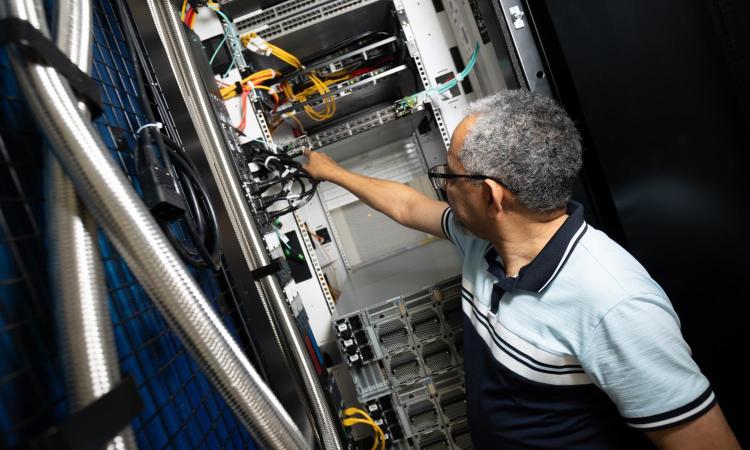

Training the AI Workforce
The AI Makerspace takes a dedicated approach to workforce development through curriculum-based study as well as independent exploration.
National Security
Harnessing the power of AI is a strategic imperative for national security. As nations strive to secure their positions as global leaders in the field, investing in AI education is critical for U.S. competitiveness.
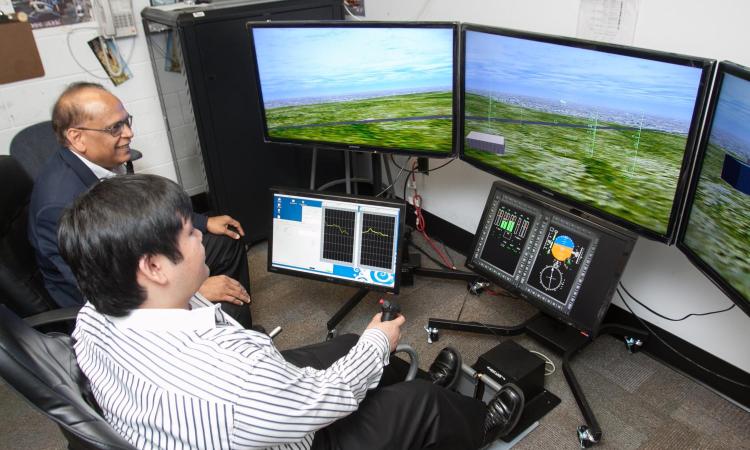

Interdisciplinary Focus
The AI Makerspace offers a unique opportunity for students to harness the power of AI technologies in ways that extend beyond traditional computing applications.
(text and background only visible when logged in)
(text and background only visible when logged in)
Technology
The Georgia Tech AI Makerspace is a dedicated computing cluster paired with NVIDIA AI Enterprise software. The software technology resides on an advanced AI infrastructure that is designed, built, and deployed by Penguin Solutions, providing a virtual gateway to a high-performance computing environment.
The first phase of the endeavor is powered by 20 NVIDIA HGX H100 systems, housing 160 NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs, one of the most powerful computational accelerators capable of enabling and supporting advanced AI and machine learning efforts. The system is interconnected with an NVIDIA Quantum-2 InfiniBand networking platform, featuring in-network computing.
Infrastructure support is led by Georgia Tech’s Partnership for an Advanced Computing Environment (PACE).
It would take a single NVIDIA H100 GPU one second to come up with a multiplication operation that would take Georgia Tech’s 50,000 students 22 years to achieve.
20 NVIDIA H100-HGX servers, each with:
- 8 x NVIDIA H100 GPUs (SXM5 form-factor)
- 2 x 32-Core Intel Sapphire Rapids CPUs (2.8 GHz)
- 2TB 4800 MHz DDR5 DRAM
- 3 x 3.84 TB NVMe storage
- 1 x ConnectX-7 IB NIC (200 Gbps)
18 NVIDIA H200-HGX servers, each with:
- 8 x NVIDIA H200 GPUs (SXM5 form-factor)
- 2 x 32-Core Intel Emerald Rapids CPUs (2.8 GHz)
- 2TB 5600 MHz DDR5 DRAM
- 8 x 3.84 TB NVMe storage
- 1 x ConnectX-7 IB NIC (200 Gbps)
Total System:
- 304 NVIDIA H100/H200 GPUs
- 2,432 Intel Sapphire Rapids CPU cores
- 76 TB 4800 MHz DDR5 DRAM
- 783.4 TB NVMe storage
(text and background only visible when logged in)
(text and background only visible when logged in)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are GPUs and CPUs?
GPUs (graphics processing units) are specialized processors designed to handle certain complex computations efficiently, commonly used in tasks such as rendering high-resolution graphics and performing parallel computations in fields like machine learning and artificial intelligence. CPUs (central processing units) are the central component of a computer responsible for executing instructions, managing tasks, and coordinating the operation of various hardware components, serving as the brain of the computer.
GPUs have become prominent due to their exceptional parallel processing capabilities, which make them highly efficient for high-performance computing (HPC) tasks. Additionally, advancements in GPU technology have led to significant improvements in graphics rendering, gaming experiences, and visual computing applications, further driving their prominence in various industries and fields.
How many GPUs are in the Georgia Tech AI Makerspace and what makes them important?
Phase I of the Georgia Tech AI Makerspace comprises a total of 160 NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs. 20 NVIDIA H100-HGX servers contain 8 GPUs each.
The benefit of GPUs is that they provide extremely performant accelerators designed specifically for AI, with a very large unified memory space that can accommodate very big models.
It’s also noteworthy that an important capability of AI is low-precision performance. These nodes provide roughly 640 petaflops (PF) of theoretical 8-bit floating-point for 8-bit integer (FP8/INT8) capability, combined with the 640 gigabytes of GPU memory per server.
Why are there both GPUs and CPUs in the Georgia Tech AI Makerspace?
CPUs and GPUs are optimized for different kinds of calculations, so it’s useful to have both available. Optimized software will perform certain steps of code on the CPU and others on the GPU to maximize performance.
CPUs are “standard” general-purpose chips that work well for many calculations. GPUs are specialized. A server cannot run without a CPU. The CPU handles all the tasks required for all software on the server to run correctly.
GPUs are accelerators with more focused computational hardware that rely on a separate host system to operate.
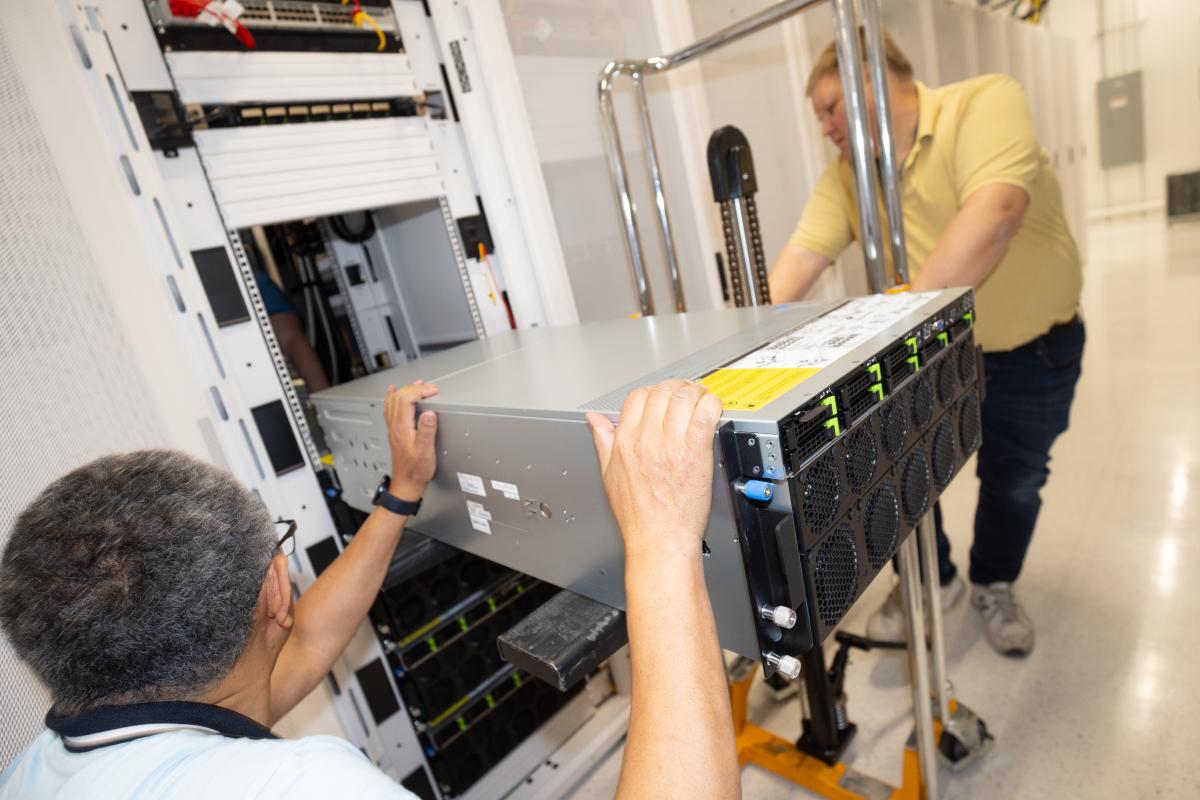

Who will manage the infrastructure of the AI Makerspace?
The AI Makerspace infrastructure will be supported by Georgia Tech’s Partnership for an Advanced Computing Environment (PACE). PACE provides sustainable leading-edge Research Computing and Data (RCD) cyberinfrastructure, software, and support for research and education requiring high performance computing and other advanced research computing infrastructure.
PACE is a collaboration between Georgia Tech faculty and the Office of Information Technology (OIT) focused on HPC.
Is the AI Makerspace scalable?
Yes. Each GPU can be physically partitioned into 7 GPUs (with 1/8 the capability of the whole). With 160 total GPUs, the AI Makerspace can provide 1,120 concurrent GPUs to allow large numbers of students access simultaneously.
How much power does the AI Makerspace require?
The new servers will draw about 140kW of power, compared to the 800kW PACE’s five existing clusters draw.
The theoretical 64-bit performance of the new hardware is 5.5 PF (petaflops, a measurement of computer speed of performing calculations). The existing PACE clusters altogether have about 4-4.5 PF of performance. This means that the new servers are significantly more energy efficient for the same computational capability than older systems.
(text and background only visible when logged in)
Related Content

Minor Degree in AI and Machine Learning Available Summer 2024
The new minor degree program is a partnership between the College of Engineering and the Ivan Allen College of Liberal Arts, teaching AI technical skills alongside ethics and policy considerations.

College Adds, Reimagines AI Courses for Undergraduates
In response to demand from its students, initiatives within faculty research, and increasing needs from industry, the College has created and reimagined more than a dozen courses to strengthen its AI and machine learning education.